NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2.4
Introduction :
In this exercise we will learn about Polynomials. Factor theorem , if p(x) is a polynomial of degree n ≥ 1 and a is any real number then
(i) x - a is a factor of p(x), if p(a) = 0, and
(ii) p(a) = 0, if x - a is a factor of p(x).
This actually follows immediately from the Remainder Theorem, but we shall not prove it here. Using by splitting the middle term.
NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials :
- NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2.1
- NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2.2
- NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2.3
- NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2.4
- NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2.5
- Extra Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Class 9 Maths Exercise 2.4 (Page-43)
Q1. Determine which of the following polynomials has ( x + 1 ) a Factor :
(i) x3 + x2 + x + 1
Solution :
Let p(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1
( x + 1 ) is a Factor of p ( x )
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
Using the factor theorem,
When p(x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1
than p( - 1 ) = ( - 1 )3 + ( - 1 )2 + ( - 1 ) + 1
= - 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 [ because - 1 + 1 = 0 , - 1 + 1 = 0 ]
= 0
∴ ( x + 1 ) is a factor of x3 + x2 + x + 1 .
(ii) x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
Solution :
Let p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
( x + 1 ) is a Factor of p ( x )
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1
than p( - 1 ) = ( - 1 )4 + ( - 1 )3 + ( - 1 )2 + ( - 1 ) + 1
= 1 - 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 [ because 1 - 1 = 0 , 1 - 1 = 0 ]
= 1
∴ ( x + 1 ) is a factor of x4 + x3 + x2 + x + 1 .
(iii) x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
Solution :
Let p(x) = x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
( x + 1 ) is a Factor of p ( x )
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1
than p( - 1 ) = ( - 1 )4 + 3 ( - 1 )3 + 3 ( - 1 )2 + ( - 1 ) + 1
= 1 + 3 × ( - 1 ) + 3 × ( 1 ) - 1 + 1
= 1 - 3 + 3 - 1 + 1
= 1
∴ ( x + 1 ) is a factor of x4 + 3x3 + 3x2 + x + 1 .
(iv) x3 - x2 - ( 2 + √2 ) x + √2
Solution :
Let p(x) = x3 - x2 - ( 2 + √2 ) x + √2
( x + 1 ) is a Factor of p ( x )
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = x3 - x2 - ( 2 + √2 ) x + √2
than p ( - 1 ) = ( - 1 )3 - ( - 1 )2 - ( 2 + √2 ) × ( - 1 ) + √2
= - 1 - 1 - ( - 2 - √2 ) + √2
= - 2 + 2 + √2 + √2 [ because - 2 + 2 = 0 ]
= 2√2
∴ ( x + 1 ) is a factor of x3 - x2 - ( 2 + √2 ) x + √2 .
Q2. Use the factor theorem to determine whether g( x ) is a factor of p( x ) in each of the following cases :
(i) p( x ) = 2x3 + x2 - 2x - 1 , g( x ) = x + 1
Solution :
Given p(x) = 2x3 + x2 - 2x - 1
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = 2x + x - 2x - 1
p(-1) = 2 ( - 1 )3 + ( - 1 )2 - 2 ( - 1 ) - 1
= - 2 + 1 + 2 - 1 [ because - 2 + 2 = 0 , - 1 + 1 = 0 ]
= 0
∴ Yes, g( x ) is a factor of p( x ) .
(ii) p( x ) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 , g( x ) = x + 2
Solution :
Given p(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1
So, x + 2 = 0
x = - 2
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1
p( - 2 ) = ( - 2 )3 + 3 ( - 2 )2 + 3 ( - 2 ) + 1
= - 8 + 3 × 4 - 6 + 1
= - 8 + 12 - 6 + 1
= - 14 + 13
= - 1
∴ No, g( x ) is not a factor of p( x ) .
(iii) p( x ) = x3 - 4x2 + x + 6 , g( x ) = x - 3
Solution :
Given p(x) = x3 - 4x2 + x + 6
So, x - 3 = 0
x = 3
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = x3 - 4x2 + x + 6
p( 3 ) = ( 3 )3 - 4 ( 3 )2 + 3 + 6
= 27 + 4 × 9 + 3 + 6
= 27 - 36 + 3 + 6
= 36 - 36
= 0
∴ Yes, g( x ) is a factor of p( x ) .
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 2
Q3. Find the value of k, if x - 1 is a factor of p( x ) in each of the following cases :
(i) p( x ) = x2 + x + k
Solution :
We have p(x) = x2 + x + k
Given x - 1 is factor of p(x)
So, x - 1 = 0
x = 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p( x ) = x2 + x + k
than p(1) = ( 1 )2 + 1 + k =0
⇒ 1 + 1 + k = 0
⇒ 2 + k = 0
⇒ k = - 2
The value of k = - 2 .
(ii) p( x ) = 2x2 + kx + √2
Solution :
We have p(x) = 2x2 + kx + √2
Given x - 1 is factor of p(x)
So, x - 1 = 0
x = 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = 2x2 + kx + √2
than p( 1 ) = 2 ( 1 )2 + k ( 1 ) + √2 = 0
= 2 × 1 + k + √2 = 0
= 2 + k + √2 = 0
= √2 + k = - 2
= k = - 2 - √2
= k = - ( 2 + √2 )
The value of k = - ( 2 + √2 ) .
(iii) p( x ) = kx2 - √2x + 1
Solution :
We have p(x) = kx2 - √2x + 1
Given x - 1 is factor of p(x)
So, x - 1 = 0
x = 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = kx2 - √2x + 1
than p( 1 ) = k ( 1 )2 - √2 ( 1 ) + 1 = 0
= k - √2 + 1 = 0
= k + 1 = √2
= k = √2 - 1
The value of k = √2 - 1 .
(iv) p( x ) = kx2 - 3x + k
Solution :
We have p(x) = kx2 - 3x + k
Given x - 1 is factor of p(x)
So, x - 1 = 0
x = 1
Using the factor theorem,
when p(x) = kx2 - 3x + k
than p( 1 ) = k ( 1 ) - 3 × 1 + k = 0
= k - 3 + k = 0
= 2k - 3 = 0
= 2k = 3
= k = \(\displaystyle \frac{3}{2}\)
The value of k = \(\displaystyle \frac{3}{2}\) .
Q4. Factorise :
(i) 12x2 - 7x + 1
Solution :
We have 12x2 - 7x + 1
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, 12x2 - 7x + 1
= 12x2 - 4x + 3x + 1
= 3 × 4 × x2 - 4x - 3x + 1 [ find the common ]
= 4x ( 3x - 1 ) - 1 ( 3x - 1 )
= ( 4x + 1 ) ( 3x - 1 )
(ii) 2x2 + 7x + 3
Solution :
We have 2x2 + 7x + 3
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, 2x2 + 7x + 3
= 2x2 + 6x + 1x + 3
= 2 × x2 + 2 × 3 × x + 1x + 3 [ find the common ]
= 2x ( x + 3 ) + 1 ( x + 3 )
= ( 2x + 1 ) ( x + 3 )
(iii) 6x2 + 5x - 6
Solution :
We have 6x2 + 5x - 6
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, 6x2 + 5x - 6
= 6x2 + 9x - 4x - 6
= 2 × 3 × x2 + 3 × 3 × x - 2 × 2 × x - 2 × 3 [ find the common ]
= 3x ( 2x + 3 ) - 2 ( 2x + 3 )
= ( 3x - 2 ) ( 2x + 3 )
(iv) 3x2 - x - 4
Solution :
We have 3x2 - x - 4
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, 3x2 - x - 4
= 3x2 - 4x + 3x - 4
= 3 × x2 - 2 × 2 × x + 3 × x - 2 × 2 [ find the common ]
= x ( 3x - 4 ) + 1 ( 3x - 4 )
= ( x + 1 ) ( 3x - 4 )
Q5. Factorise :
(i) x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
Solution :
Let p( x ) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
So, x - 1 = 0
x = 1
When p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
than, ( 1 )3 - 2( 1 )2 - ( 1 ) + 2
= 1 - 2 × 1 - 1 + 2
= 1 - 2 - 1 + 2 [ because - 1 + 1 = 0 , - 2 + 2 = 0 ]
= 0
∴ ( x - 1 ) is a factor of p( x )
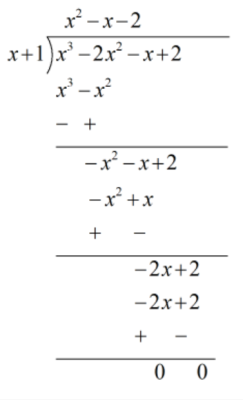
So, p( x ) = x2 - x - 2
x2 - x - 2
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, x2 - x - 2
= x2 - 2x + x - 2 [ find the common ]
= x ( x - 2 ) + 1 ( x - 2 )
= ( x + 1 ) ( x - 2 )
∴ ( x + 1 ) ( x + 1 ) ( x - 2 ) is a factor of p( x ) .
(ii) x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
Solution :
Let p( x ) = x3 - 3x2 - 9x - 5
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
When p(x) = x3 - 2x2 - x + 2
than, ( - 1 )3 - 3( - 1 )2 - 9( - 1 ) - 5
= - 1 - 3 × 1 + 9 - 5
= - 1 - 3 + 9 - 5
= - 9 + 9
= 0
∴ ( x + 1 ) is a factor of p( x )
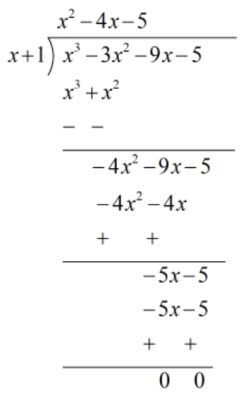
So, p( x ) = x2 - 4x - 5
x2 - 4x - 5
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, x2 - 4x - 5
= x2 - 5x + x - 5 [ find the common ]
= x ( x - 5 ) + 1 ( x - 5 )
= ( x + 1 ) ( x - 5 )
∴ ( x + 1 ) ( x - 5 ) ( x + 1 ) is a factor of p( x ) .
(iii) x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
Solution :
Let p( x ) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
So, x + 1 = 0
x = - 1
When p(x) = x3 + 13x2 + 32x + 20
than, ( - 1 )3 + 13( - 1 )2 + 32( - 1 ) + 20
= - 1 + 13 × 1 - 32 + 20
= - 1 + 13 - 32 + 20
= - 33 + 33
= 0
∴ ( x + 1 ) is a factor of p( x )
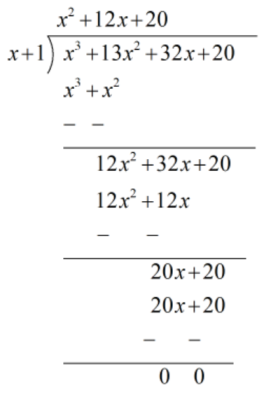
So, p( x ) = x2 + 12x + 20
x2 + 12x + 20
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, x2 + 12x + 20
= x2 + 10x + 2x + 20
= x ( x + 10 ) + 2 ( x + 10 )
= ( x + 2 ) ( x + 10 )
∴ ( x + 1 ) ( x + 2 ) ( x + 10 ) is a factor of p( x ) .
(iv) 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
Solution :
Let p( y ) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
So, y + 1 = 0
y = - 1
When p(y) = 2y3 + y2 - 2y - 1
than, 2( - 1 )3 + ( - 1 )2 - 2( - 1 ) - 1
= 2 × - 1 + 1 + 2 - 1
= - 2 + 1 + 2 - 1 [ because - 2 + 2 = 0 , 1 - 1 = 0 ]
= 0
∴ ( y + 1 ) is a factor of p( x )
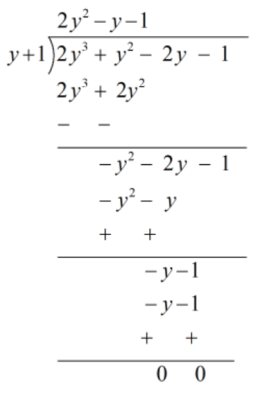
So, p( y ) = 2y2 - y - 1
2y2 - y - 1
[ Using the splitting the middle term method ]
So, 2y2 - y - 1
= 2y2 - 2y + y - 1
= 2y ( y - 1 ) + 1 ( y - 1 )
= ( 2y + 1 ) ( y - 1 )
∴ ( y + 1 ) ( 2y + 1 ) ( y - 1 ) is a factor of p( y ) .
