NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.1
Introduction :
In this chapter you come to know about polygons. A simple curved made up of only line segments is called polygon. Polygons are classified according to the number of sides or vertices they have.
A diagonal is a line segment connecting two non- consecutive vertices of a polygon. There are two types of polygons named convex and concave polygons.
NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals :
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.1
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.2
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.3
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.4
Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.1
Q1. Given here are some figures.
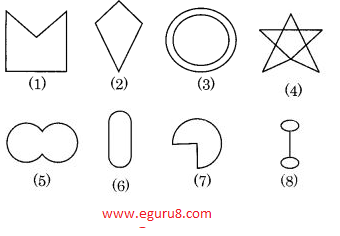
Classify each of the above figure on the basis of the following:
(a) Simple curve
(b) Simple closed curve
(c) Polygon
(d) Convex polygon
(e) Concave polygon
Solution: a) Simple curve - 1,2,5,6,7
(b) Simple closed curve - 1,2,5,6,7
(c) Polygon - 1,2
(d) Convex polygon - 2
(e) Concave polygon -1
Q2. How many diagonals does each of the following have?
(a) A convex quadrilateral
(b) A regular hexagon
(c) A triangle
Solution:
(a) A convex quadrilateral
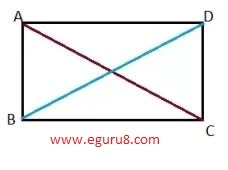
from the above figure, the diagonals formed in a convex quadrilateral is 2( AC and BD).
(b) A regular hexagon
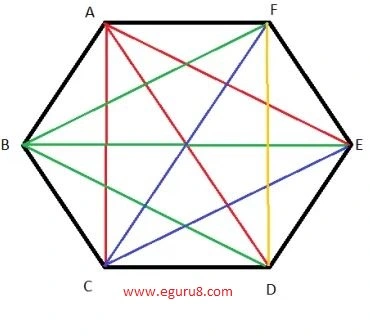
from the above figure, the diagonals formed in a regular hexagon is 9( AC, AD, AE, BF, BE, BD, CF,CE and DF).
(c) A triangle
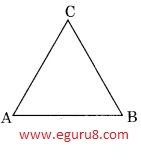
from the above figure, the diagonal formed in a triangle is 0.
Q3. What is the sum of the measures of the angles of a convex quadrilateral? Will this property hold if the quadrilateral is not convex? (Make a non-convex quadrilateral and verify)
Solution: First we draw a convex quadrilateral
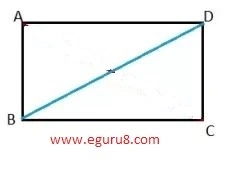
In quadrilateral ABCD,
∠A+∠B+∠C+∠D
∠1+∠2+∠3+∠4+∠5+∠6
arranging according to ΔABD and ΔBCD
(∠1+∠2+∠6) + (∠3+∠4+∠5)
∠1+∠2+∠6 = 180°( By angle sum property of Δ)
∠3+∠4+∠5 = 180°( By angle sum property of Δ)
s0, 180°+180° = 360°
In case of Non Convex Quadrilateral
First we draw a Non Convex Quadrilateral

considering ΔABD and ΔBCD
∠1+∠2+∠3 = 180°( By angle sum property of Δ)
∠4+∠5+ ∠6 = 180°( By angle sum property of Δ)
So,180°+180° = 360°
From the above observation, this property hold if the quadrilateral is not convex.
Q4.Examine the table. (Each figure is divided into triangles and the sum of the angles reduced from that).
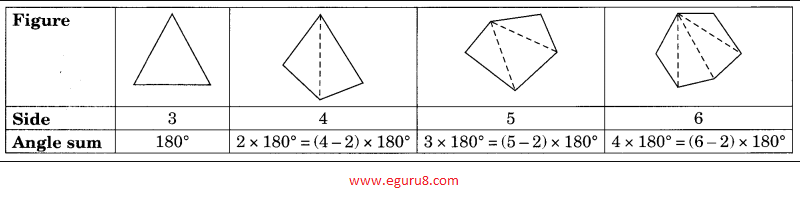
What can you say about the angle sum of a convex polygon with number of sides?
(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) n
Solution: From the table, the angle sum of a convex polygon of n side is = (n-2) × 180°
(a) 7 = (n-2) × 180°
= (7-2) × 180°
=5× 180°
= 900°
(b) 8 = (n-2) × 180°
= (8-2) × 180°
= 6× 180°
= 1080°
(c) 10 = (n-2) × 180°
= (10-2) × 180°
= 8× 180°
=1440°
(d) n= (n-2) × 180°
Q5. What is a regular polygon? State the name of a regular polygon of
(i) 3 sides
(ii) 4 sides
(iii) 6 sides
Solution: A polygon with equal side and equal angle is called regular polygon.
i) a polygon with 3 side is called equilateral triangle.
ii) a polygon with 4 side is called square.
iii) a polygon with 6 side is called hexagon.
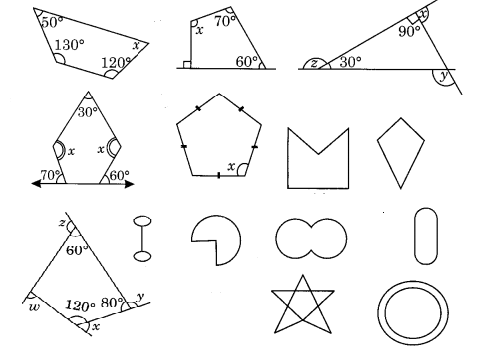
Q6. Find the angle measure x in the following figures:
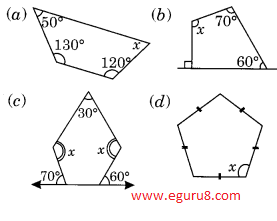
Solution:
a) Angle sum of Quadrilateral = 360°
50°+130°+120°+x = 360°
180°+ 120°+x =360°
300°+ x = 360°
x = 360° - 300°
x = 60°
b) Angle sum of Quadrilateral = 360°
70°+ 60°+ 90° +x = 360°
220°+x = 360°
x = 360° - 220°
x = 140°
c) Angle sum of pentagon = 540°
x + x+ 30 +110°+ 120° = 540° ( 180° - 70° = 110° - by linear pair) ( 180°- 60° = 120° - by linear pair)
2x + 260° = 540°
2x = 540°- 260°
2x = 280°
x = \(\displaystyle \frac{{280°}}{2}\)
x = 140°
d) Angle sum of regular pentagon = 540°
x + x +x +x +x = 540°
5x = 540°
x = \(\displaystyle \frac{{540°}}{5}\)
x = 108°
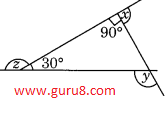
Q7. (a) Find x + y + z
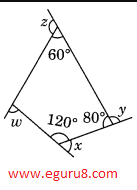
b) Find x + y + z + w
Solution:
a)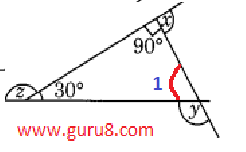
∠1+90°+30° = 180° (angle sum property of triangle)
∠1+120° = 180°
∠1 = 180° - 120° = 60°
Using linear pair
∠x + 90° = 180°
∠x = 180° - 90°
∠x = 90°
∠1+∠y = 180°
60°+∠y= 180°
∠y = 180°- 60°
∠y = 120°
∠z+30° = 180°
∠z = 180° - 30°
∠z = 150°
now,
x + y + z
90° + 120° + 150°
= 360°
so, x + y + z = 360°
b)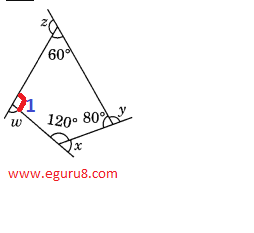
∠1+120°+80° + 60° = 360° (angle sum property of quadrilateral)
∠1+260° = 360°
∠1 = 360° - 260°
∠1 = 100°
Using linear pair
∠x + 120° = 180°
∠x = 180° - 120°
∠x = 60°
∠y + 80° = 180°
∠y = 180° - 80°
∠y = 100°
∠z + 60° = 180°
∠z = 180° - 60°
∠z = 120°
∠w+∠1 = 180°
∠w + 100° = 180°
∠w = 180° - 100°
∠w = 80°
so, x + y + z +w
= 60° + 100° + 120° + 80°
= 360°
thus, x + y + z +w = 360°
NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals :
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.1
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.2
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.3
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.4