NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Cubes and Cube Roots Exercise 7.1
Introduction:
In this exercise/article we will learn about cube and cube roots. Cube is 3d picture of square and you will find the cube and cubes roots in this exercise and find cube and cube roots through prime factorisation method and find the perfect cube. You will learn cubes then do this exercise .
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Cubes and Cube Roots :
- NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Cubes and Cube Roots Exercise 7.1
- NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Cubes and Cube Roots Exercise 7.2
Class 8 Maths Exercise 7.1 (Page-114)
Q1. Which of the following numbers are not perfect cubes ?
(i) 216
Solution :
Given 216
we need to find the not perfect cube of 216

216 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 ×3
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \underline{{3\,\times \,3\,\times \,3}}\)
= 23 × 33
= 2 × 3
= 6
So, the perfect cube of 216 is 6
(ii) 128
Solution :
Given 128
we need to find the not perfect cube of 128

128 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,2\)
= 23 × 23 × 2
= 2 × 2 × 2
= 8
So, 128 is not a perfect cube
(iii) 1000
Solution :
Given 1000
we need to find the not perfect cube of 1000

1000 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \underline{{5\,\times \,5\,\times \,5}}\,\times \,5\)
= 23 × 53 × 5
= 2 × 5
= 10
So, the perfect cube of 1000 is 10
(iv) 100
Solution :
Given 100
we need to find the not perfect cube of 100

100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{5\,\times \,5}}\)
= 22 × 52
= 2 × 5
= 10
So, 100 is not a perfect cube
(v) 46656
Solution :
Given 46656
we need to find the not perfect cube of 46656
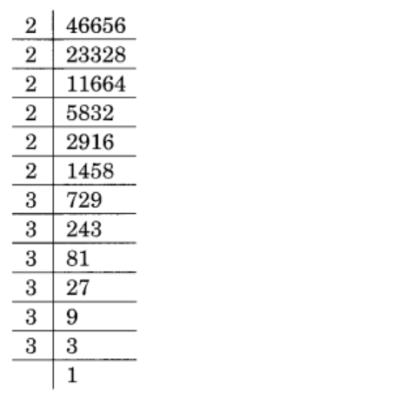
46656 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{3\,\times \,3\,\times \,3\,}}\times \,\underline{{3\,\times \,3\,\times \,3}}\)
= 23 × 23 × 33 × 33
= 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
= 36
So, the perfect cube of 46656 is 36
Q2. Find the smallest number by which each of the following numbers must be multiplied to obtain a perfect cube.
(i) 243
Solution :
Given 243
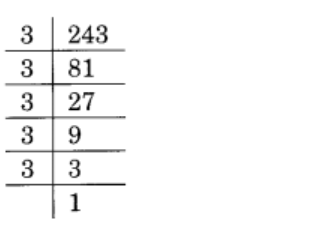
243 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{3\,\times \,3\,\times \,3}}\,\times \,\underline{{3\,\times \,3}}\)
= 33 × 32
∴ It must be multiplied by 3 to obtain a perfect cube
So, answer is 3
(ii) 256
Solution :
Given 256
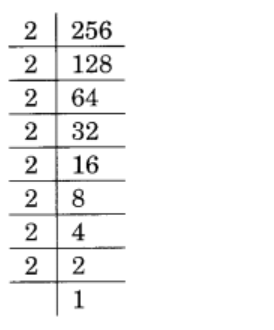
256 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{2\,\times \,2}}\)
= 23 × 23 × 22
∴ It must be multiplied by 2 to obtain a perfect cube
= So, answer is 2
(iii) 72
Solution :
Given 72
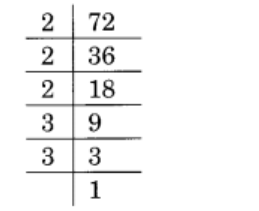
72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{3\,\times \,3}}\)
= 23 × 32
∴ It must be multiplied by 3 to obtain the perfect cube
So, answer is 3
(iv) 675
Solution :
Given 675
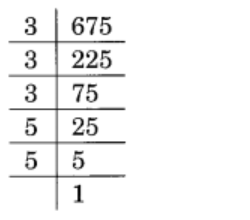
675 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 5
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{3\,\times \,3\,\times \,3}}\,\times \,\underline{{5\,\times \,5}}\)
= 33 × 52
∴ It must be multiplied by 5 to obtain a perfect cube
= So, answer is 5
(v) 100
Solution :
Given 100

100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{5\,\times \,5}}\)
= 22 × 52
= 2 × 5 = 10 [ each multiplied ]
∴ It must be multiplied by 10 to obtain a perfect cube
So, answer is 10
Q3. Find the smallest number by which each of the following numbers must be divided to obtain a perfect cube.
(i) 81
Solution :
Given 81
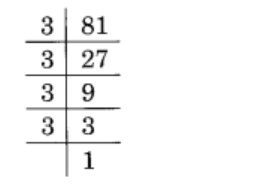
81 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{3\times \,3\,\times \,3}}\,\times \,3\,\)
= 33 × 3
∴ 81 must be divided by 3 to obtain a perfect cube
So, answer is 3
(ii) 128
Solution :
Given 128
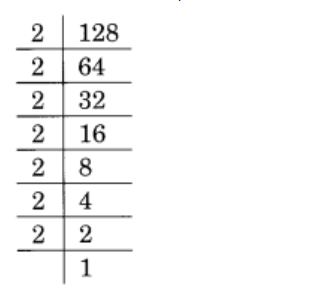
128 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{2\,\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,2\,\)
= 23 × 23 × 2
∴ 128 must be divided by 2 to obtain a perfect cube
So, answer is 2
(iii) 135
Solution :
Given 135
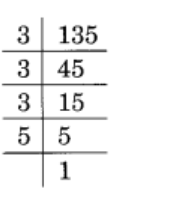
135 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 5
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{3\times \,3\,\times \,3}}\,\times \,5\,\)
= 33 × 5
∴ 135 must be divided by 5 to obtain a perfect cube
So, answer is 5
(iv) 192
Solution :
Given 192
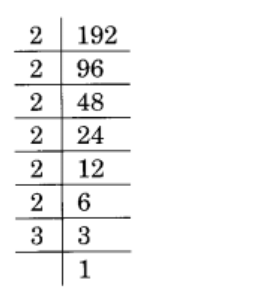
192 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{2\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,3\)
= 23 × 23 × 3
∴ 192 must be divided by 3 to obtain a perfect cube
So, answer is 3
(v) 704
Solution :
Given 704
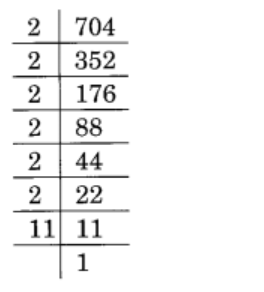
704 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 11
= \(\displaystyle \underline{{2\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,\underline{{2\times \,2\,\times \,2}}\,\times \,11\)
= 23 × 23 × 11
∴ 704 must be divided by 11 to obtain a perfect cube
Q4. Parikshit makes a cuboid of plasticine of sides 5cm, 2cm , 5cm. How many such cuboid will he need to form a cube ?
Solution :
Given , side of cuboid is 5cm, 2cm and 5cm
[ Volume of the cuboid = Length × breadth × height ]
= 5 × 2 × 5
= 50
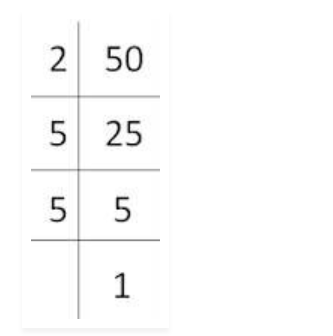
50 = 2 × 5 × 5
= 2 × 52
= 2 × 2 × 5 [ we need 22 and 5 for complete perfect cube of 2 and 5 ]
= 20 cuboids
So, answer is 20 cuboids .
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Cubes and Cube Roots :